数据结构作业四 表达式树
从中缀表达式构建二叉树

问题分析 & 解决方案
题目要求输入一个中缀表达式,构建其相应的表达式树,并输出验证。
表达式树的特点是操作符所对应的两个操作数分别对应于操作符的左孩子和右孩子。直接从中缀表达式构建相对困难,考虑此前已经有过从中缀表达式构建后缀表达式的经验,以及后缀表达式运算符位于操作数之后的特点,可以从后缀表达式入手解决该问题。
通过对表达式树和后缀表达式的观察不难得出可以通过以下方法从后缀表达式得到表达式树:后缀表达式自后向前遍历,在右节点优先级高于左节点的前提下根据当前遍历元素类型进行以下两种操作:
- 当前元素为运算符,将运算符构建为树的一个节点,若为右孩子则将操作节点压栈。无论是左孩子还是右孩子,之后操作节点转移到新建节点。
- 当前元素为操作数,将运算符构建为树的一个节点,若为左孩子则操作节点转移到栈顶节点,栈弹出。
最终解决方案为:将输入的中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式,再按照上述规则构建整个表达式树。同时还要注意最终树形的输出。
算法设计
参照课本,构建节点类、二叉树类,并对其中的相关函数进行实现,另外准备一个函数将中缀表达式构建为后缀表达式,并进行树的构建。
课本中并没有节点深度这个属性,但终端输出时节点如果具有深度属性会非常方便,于是对其进行了补充,并添加了相关的函数对节点的深度进行更新,与高度更新一致调用。这里需要注意,高度的更新是自下向上,深度的更新则是自上而下,需要一个遍历的过程,我在具体实现的过程中采用了层遍历的方式。
终端输出的思考
如何在终端中输出是一个比较困难的问题。因为终端输出一行后不能回退到上一行,如果不对各个元素提前保存,就要在遍历的时候进行一些小操作。同时输出时空格的控制也需要细节处理。在这里简单介绍一下我的做法。
我采用的方法是使用层遍历的方法,同时为每一个节点增加横坐标,遍历节点的同时更新节点的横坐标,根据横坐标和深度的情况判断是否需要换行和需要输出空格的数量。伴随着二叉树深度的增加,每层的节点呈指数级增长,如果一开始输出的节点之间的间隔控制的不好,后续的输出就会变得困难。
高度为n的满二叉树,最底层有2^n个节点,考虑到底层节点不能直接相邻(至少隔一个空格),所以最底层所占字符总长为2^(n+1)个。现假设我们按照满二叉树的形式对整个树进行输出,输出区域为长为2^(n+1)个字符,高为n行的矩形,根节点位于整个图形的对称轴上,故根节点的横坐标为2^n,同理可推得根节点的左孩子的横坐标为2^(n-1)。考虑到在满二叉树的情况下每层节点之间的间隔是一定值,且为该层最左侧节点的横坐标,故在已知一个节点的横坐标及下一层的固定节点间隔的情况下,可以更新出该节点两个孩子的横坐标。
按照上述方法在进行层遍历的同时对节点横坐标进行更新,记录上一个节点的横坐标,即使二叉树不是完全二叉树也能够正常输出形状。当然,因为终端的宽度一定,当层数大到最后一排无法显示的时候形状一定会发生改变。
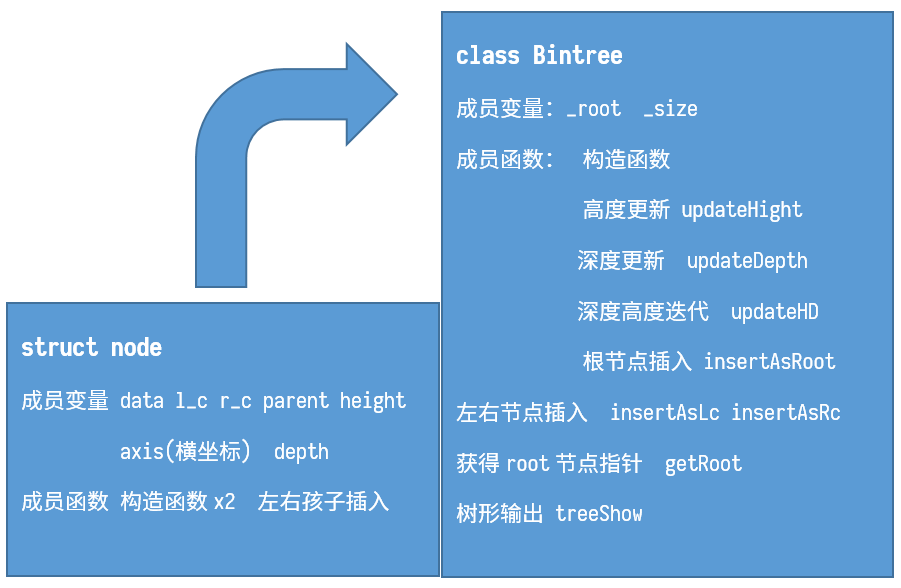
流程图
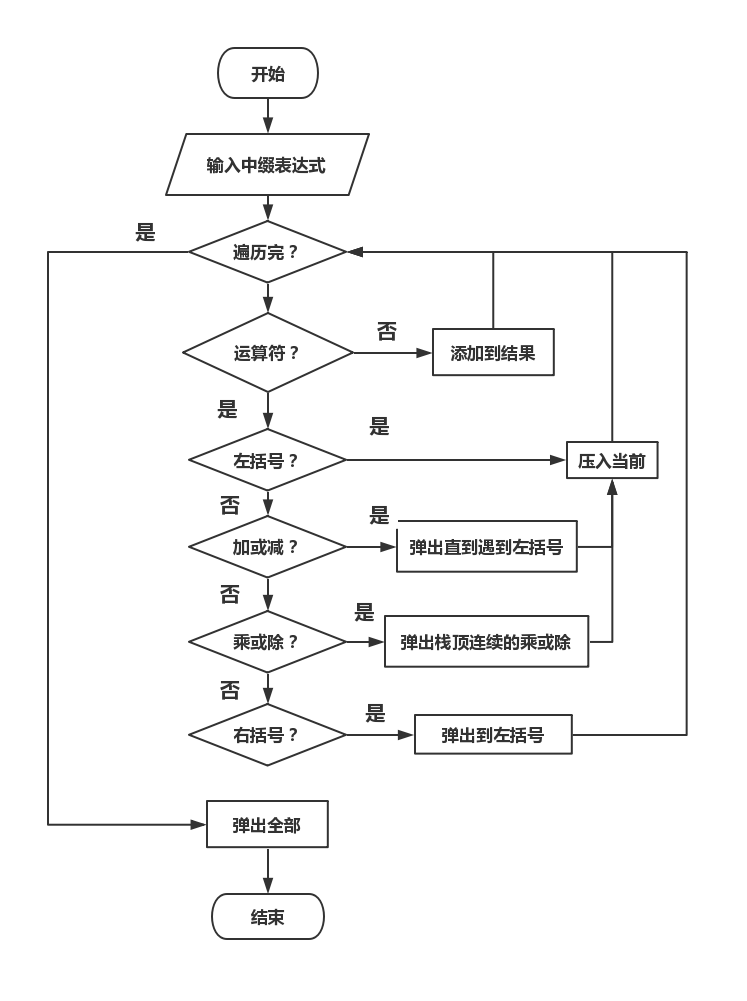
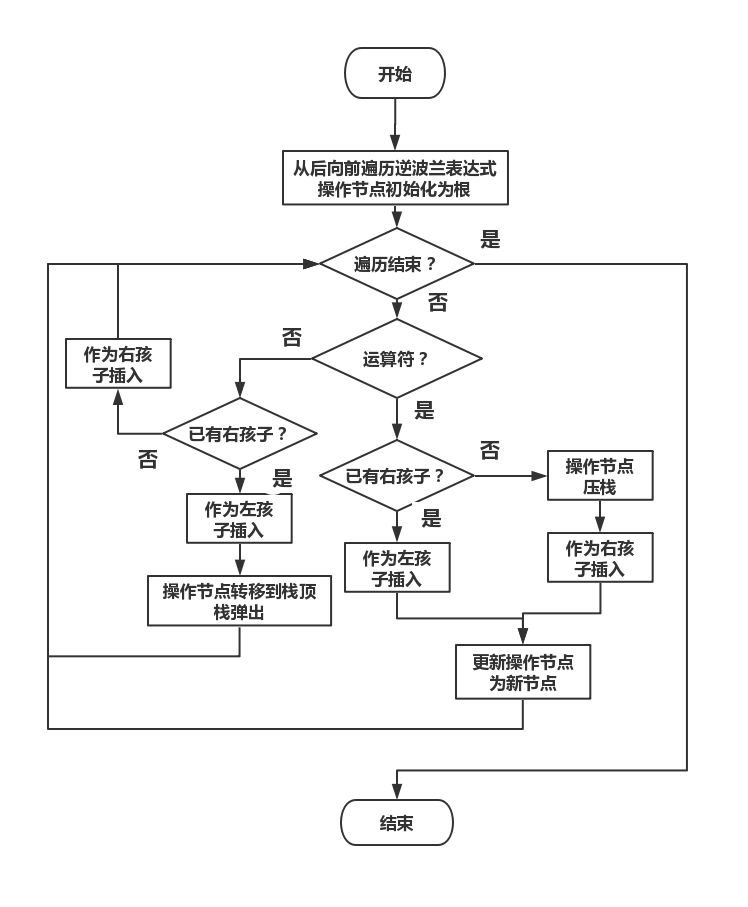
编程实现
共编写了三个文件:node.h、Bintree.h、main.cpp
1.node.h
#define stature(p) ((p) ? (p)->height : -1)
//节点指针的判断
#define IsLc(x) ((x)->parent && ((x) == (x)->parent->l_c))
#define IsRc(x) ((x)->parent && ((x) == (x)->parent->r_c))
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//NULL 在何处定义?
template <typename T>
struct node{
T data;
node<T>* parent;
node<T>* l_c;
node<T>* r_c;
int height;
int axis; //打印时空格
int depth; //深度非常重要!
//构造函数
node():parent(NULL), l_c(NULL), r_c(NULL), height(0), axis(0), depth(0){}
node(T e, node<T>* p=NULL, node<T>* lc=NULL, node<T>* rc = NULL, int h=0):data(e),parent(p),l_c(lc),r_c(rc),height(h),axis(0),depth(0){}
node<T>* insertLc(T const&);
node<T>* insertRc(T const&);
};
//两个插入的实现
template <typename T>
node<T>* node<T>::insertLc(T const& e){
return l_c = new node(e, this);
}
template <typename T>
node<T>* node<T>::insertRc(T const& e){
return r_c = new node(e, this);
}
2.bintree.h
#include "node.h"
#include <queue>
template <typename T>
class Bintree{
node<T>* _root;
int _size;
public:
//构造
Bintree():_root(NULL),_size(0){}
//更新高度、深度
void updateHight(node<T> *x);
void updateDepth(node<T>* x);
void updateHD(node<T> *x);
//节点插入e
node<T>* insertAsRoot (T const& e);
node<T>* insertAsLc(node<T>* x, T const& e);
node<T>* insertAsRc(node<T>* x, T const& e);
//获得节点指针
node<T>* getRoot();
// node<T>* getLc(node<T>* x);
// node<T>* getRc(node<T>* x);
//上面这两个没有用了....
//大小
int size(){ return _size;}
//表达
void treeShow();
// void createBlank(int n);
};
template <typename T>
void Bintree<T>::updateHight(node<T>* x){
x->height = 1 + (stature(x->l_c) > stature(x->r_c) ? stature(x->l_c) : stature(x->r_c));
}
template <typename T>
void Bintree<T>::updateDepth(node<T>* x){
if(x == _root) return;
x->depth = 1 + x->parent->depth;
}
template <typename T>
void Bintree<T>::updateHD(node<T>* x){
node<T>* y = x;
while(x){
updateHight(x);
x = x->parent;
}
queue< node<T>* > tmp;
if(y){
tmp.push(y);
while(!tmp.empty()){
updateDepth(tmp.front());
if(tmp.front()->l_c)
tmp.push(tmp.front()->l_c);
if(tmp.front()->r_c)
tmp.push(tmp.front()->r_c);
tmp.pop();
}
}
}
template <typename T>
node<T>* Bintree<T>::insertAsRoot(T const& e){
_size = 1;
return _root = new node<T>(e);
}
template <typename T>
node<T>* Bintree<T>::insertAsLc(node<T>* x, T const& e){
_size++;
x->insertLc(e);
updateHD(x);
return x->l_c;
}
template <typename T>
node<T>* Bintree<T>::insertAsRc(node<T>* x, T const& e){
_size++;
x->insertRc(e);
updateHD(x);
return x->r_c;
}
template <typename T>
node<T>* Bintree<T>::getRoot(){
return _root;
}
template <typename T>
void Bintree<T>::treeShow(){
int num = 1;
int n = _root->height; //获得高度
while(n--){ num *= 2;}
//层遍历
queue< node<T>* > tmp;
node<T>* curr;
int last_axis = 0, last_depth = 0;
if(_root)
tmp.push(_root);
while(!tmp.empty()){
// if(last != tmp.front()->parent){
// num /=2;
// cout << endl;
// for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
// cout << ' ';
// }
// else
// for(int i = 0; i < 2*num-1; i++)
// cout << ' ';
//改为从父亲那里得到横坐标
//新的一层 改变num 同时last_axis清零 (通过比较深度)
curr = tmp.front();
if(last_depth != curr->depth){
num/=2;
last_axis = 0;
cout << endl;
}
if(curr == _root)
_root->axis = num;
else{
if(IsLc(curr))
curr->axis = curr->parent->axis - num;
else
curr->axis = curr->parent->axis + num;
}
//输出空格 需要减一
for(int i = 0; i < curr->axis - last_axis - 1; i++)
cout << ' ';
cout << curr->data;
last_depth = curr->depth;
last_axis = curr->axis;
if(curr -> l_c)
tmp.push(curr->l_c);
if(curr -> r_c)
tmp.push(curr->r_c);
tmp.pop();
}
return ;
}
// template <typename T>
// void Bintree<T>::createBlank(int n){
// while(n--)
// cout << ' ';
// return ;
// }
3.main.cpp
#include "bintree.h"
#include <string>
#include <stack>
//从中缀表达式构建
void create_from_infix(Bintree<char>& my_tree){
string strs, res;
stack<char> tmp; //运算符
cout << "Input infix expression :" << endl;
cin >> strs;
for(int i = 0; i < strs.size(); i++){
if(strs[i] >= '0')
res += strs[i];
else if(strs[i] == '(')
tmp.push(strs[i]);
else if(strs[i] == ')'){
while(tmp.top() != '('){
res += tmp.top();
tmp.pop();
}
tmp.pop(); //清除多余的'('
}
else if(strs[i] == '+' || strs[i] == '-'){
while(!tmp.empty()){
if(tmp.top() == '(')
break; //左括号额外注意
res += tmp.top();
tmp.pop();
}
tmp.push(strs[i]); //当前操作的运算符入栈
}
else if(strs[i] == '*' || strs[i] == '/'){
while(!tmp.empty()){
if(tmp.top() == '(' || tmp.top() == '+' || tmp.top() == '-')
break; //不能全部输出
res += tmp.top();
tmp.pop();
}
tmp.push(strs[i]); //入栈当前运算符
}
}
//栈中多余运算符
while(!tmp.empty()){
res += tmp.top();
tmp.pop();
}
cout << "Postfix expression is :" << endl;
cout << res << endl;
//开始造树
my_tree.insertAsRoot(res[res.size()-1]);
node<char>* x = my_tree.getRoot();
stack<node<char>*> nodes;
nodes.push(x); //防止最后一个操作数访问错误
for(int i = res.size()-2; i >= 0; i--){
if(res[i] >= '0'){
//数字或者字母作为左孩子插入时需要向上返回
if(x->r_c){
my_tree.insertAsLc(x, res[i]);
x = nodes.top();
nodes.pop();
}
else
my_tree.insertAsRc(x, res[i]);
}
else{
//字符一定会移动
if(x->r_c)
x = my_tree.insertAsLc(x, res[i]);
else{
nodes.push(x);
x = my_tree.insertAsRc(x, res[i]);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
Bintree<char> my_tree;
create_from_infix(my_tree);
cout << "Tree is:"<<endl;
my_tree.treeShow();
}
//封装的意义只是为了自动更新高度?删除更加方便?
QT图形化界面
初次接触QT,花费了较多的时间来了解Qt的使用。对QpaintEvent理解的不是很透彻,实现的时候参考了网上的一些代码。程序使用了此前编写的二叉树类,中缀表达式转化为二叉树部分也与控制台程序一致。
程序实现
Qt项目使用了此前编写的二叉树头文件,draw.cpp、main.cpp、draw.h实现如下:
1.draw.h
#ifndef DRAW_H
#define DRAW_H
#include <QMainWindow>
#include <QPaintEvent>
#include "bintree.h"
namespace Ui {
class draw;
}
class draw : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Bintree<char> my_tree;
QPaintEvent * tmp;
explicit draw(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~draw();
void createTree();
void paintEvent(QPaintEvent *);
private:
Ui::draw *ui;
signals:
public slots:
// void paintEvent(QPaintEvent *);
// void createTree();
//void showTree(bool checked);
void createClicked();
};
#endif // DRAW_H
2.draw.cpp
#include "draw.h"
#include "ui_draw.h"
#include <QPainter>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <QString>
#include <QtDebug>
#include <QChar>
#include <QtCore>
draw::draw(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::draw)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
//this->connect(ui->pushButton, SIGNAL(clicked(bool)), this, SLOT(createTree()));
this->connect(ui->huizhi, SIGNAL(clicked(bool)), this, SLOT(createClicked()));
}
draw::~draw()
{
delete ui;
}
void draw::createClicked(){
createTree();
paintEvent(tmp);
update();
}
void draw::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *)
{
QPainter painter(this);
node<char>* x = my_tree.getRoot();
node<char>* curr;
if(x){
//层遍历第一遍
int last_axis = 0, last_depth = 0;
int num = 1, n = x->height;
while(n--) num *= 2;
queue<node<char>* > tmp;
//画线
tmp.push(x);
while(!tmp.empty()){
curr = tmp.front();
if(last_depth != curr->depth){
num/=2;
last_axis = 0;
}
if(curr == x)
curr->axis = num;
else{
if(IsLc(curr))
curr->axis = curr->parent->axis - num;
else
curr->axis = curr->parent->axis + num;
}
last_depth = curr->depth;
last_axis = curr->axis;
if(curr->l_c)
tmp.push(curr->l_c);
if(curr->r_c)
tmp.push(curr->r_c);
tmp.pop();
if(x == curr)
continue; //根节点不用画线
painter.drawLine(30*curr->axis+30, 130+100*curr->depth, 30*curr->parent->axis+30, 130+100*curr->parent->depth);
}
//层遍历第二遍 画节点
tmp.push(x);
while(!tmp.empty()){
curr = tmp.front();
painter.setBrush(Qt::green);
painter.drawEllipse(30*curr->axis, 100+100*curr->depth,60,60);
painter.drawText(30*curr->axis+25, 100*curr->depth+135, QChar(curr->data));
qDebug()<<QChar(curr->data)<<endl;
if(curr->l_c)
tmp.push(curr->l_c);
if(curr->r_c)
tmp.push(curr->r_c);
tmp.pop();
}
}
}
void draw::createTree()
{
//QString str = ui->line->toPlainText().toStdString().data(); //我佛了
QString str = ui->line->text();
// QString res;
std::string res;
std::string strs = str.toStdString();
stack<char> tmp;
for(int i = 0; i < strs.size(); i++){
if(strs[i] >= '0')
res += strs[i];
else if(strs[i] == '(')
tmp.push( strs[i]);
else if(strs[i] == ')'){
while(tmp.top() != '('){
res += tmp.top();
tmp.pop();
}
tmp.pop(); //清除多余的'('
}
else if(strs[i] == '+' || strs[i] == '-'){
while(!tmp.empty()){
if(tmp.top() == '(')
break; //左括号额外注意
res += tmp.top();
tmp.pop();
}
tmp.push(strs[i]); //当前操作的运算符入栈
}
else if(strs[i] == '*' || strs[i] == '/'){
while(!tmp.empty()){
if(tmp.top() == '(' || tmp.top() == '+' || tmp.top() == '-')
break; //不能全部输出
res += tmp.top();
tmp.pop();
}
tmp.push(strs[i]); //入栈当前运算符
}
}
//栈中多余运算符
while(!tmp.empty()){
res += tmp.top();
tmp.pop();
}
//开始造树
my_tree.insertAsRoot(res[res.size()-1]);
node<char>* x = my_tree.getRoot();
stack<node<char>*> nodes;
nodes.push(x);
for(int i = res.size()-2; i >= 0; i--){
if(res[i] >= '0'){
//数字或者字母作为左孩子插入时需要向上返回
if(x->r_c){
my_tree.insertAsLc(x, res[i]);
x = nodes.top();
nodes.pop();
}
else
my_tree.insertAsRc(x, res[i]);
}
else{
//字符一定会移动
if(x->r_c)
x = my_tree.insertAsLc(x, res[i]);
else{
nodes.push(x);
x = my_tree.insertAsRc(x, res[i]);
}
}
}
}
3.main.cpp
#include "draw.h"
#include <QApplication>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
draw w;
w.show();
return a.exec();
}
运行效果
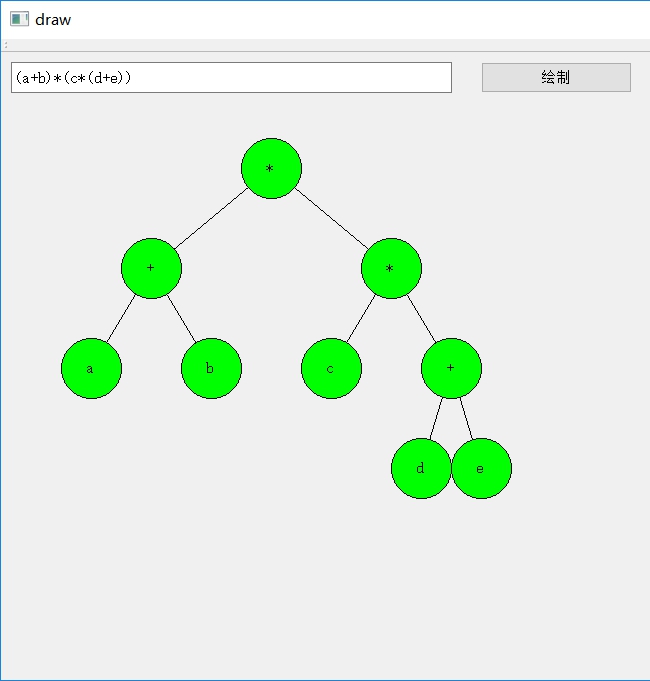
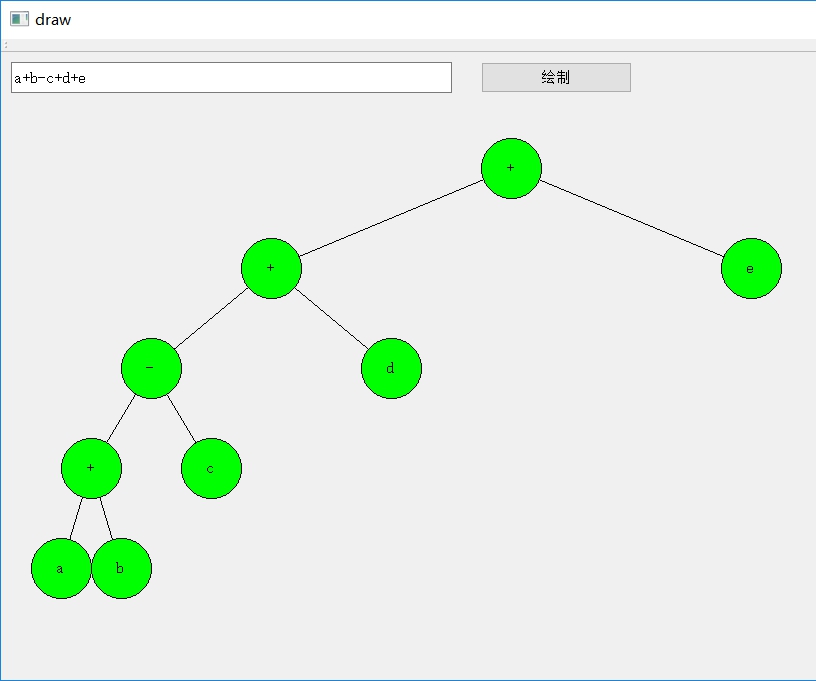
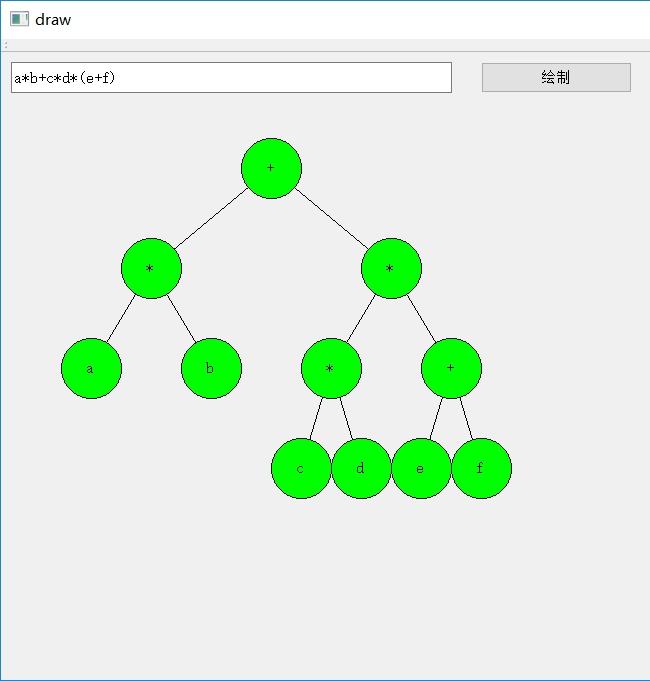
两个参考链接:
总结体会
这次作业因为事先没有考虑到横坐标的问题,遍历更新横坐标的代码写了两遍,其实这个部分完全可以作为一个成员函数写在类中,不过当我发现这个问题的时候第二遍已经写了一半多了,所以就没有改。大部分时间都去研究Qt了,所以构建树的部分可能会有漏洞。由于时间紧迫Qt程序就没有多做细节处理,另外报告撰写的质量也较低。
Qt程序不是生成图片,而是调用画笔,所以当深度过大之后会有很大部分看不到,而且经某人测试,层数达到十几层之后程序会直接bug,具体是那个地方越界还没有时间判断。现在有一个无限画布的想法但是还没有尝试去实现。总之收获还是蛮大的。
- 有时候先画出来流程图简化过程之后再写代码效率会更高。
- 面对新领域而又不需要实现特别困难的功能时:犹豫,就会败北,头铁,就会白给。